How to Conduct Stock Audits: A Step-by-Step Guide from Practical Experience
- D.K. Malhotra

- Aug 24
- 5 min read
Stock Audit has emerged as one of the most critical financial control tools for modern businesses, banks, and financial institutions. With organizations expanding across geographies, working with multiple vendors, and maintaining vast inventories, the verification and valuation of stock has become a necessity—not just for compliance, but also for operational efficiency.
This blog explains the purpose, process, and benefits of stock audits in detail, combining industry knowledge with practical experience. Whether you are a bank evaluating borrowers, or a business securing your supply chain, this guide will give you a clear roadmap.
What is a Stock Audit?
A stock audit is the independent verification of inventories and related records to ensure accuracy, compliance, and transparency. It covers:
Physical stock verification of raw materials, finished goods, and work-in-progress (WIP).
Compliance audits to check whether stock management procedures align with regulatory and internal policies.
Associated process audits to evaluate inventory control, storage, and stock movement documentation.
Stock audits are conducted for:
Businesses – to strengthen internal controls and prevent pilferage.
Banks & financial institutions – to safeguard loans and working capital extended against hypothecated stock.
Regulatory compliance – as mandated by RBI and other authorities for borrowers beyond certain thresholds.
Importance of Stock Audits
✅ Protects assets like raw material, finished stock, and machinery.
✅ Assures banks about the borrower’s financial health.
✅ Prevents fraud, pilferage, and stock manipulation.
✅ Identifies slow-moving, obsolete, or dead stock.
✅ Supports better financial planning through accurate inventory valuation.
✅ Strengthens multi-location control across warehouses, dealers, and agent premises.
Fact 1: According to RBI guidelines, banks must conduct periodic stock audits of large borrowers to protect exposure against secured assets.
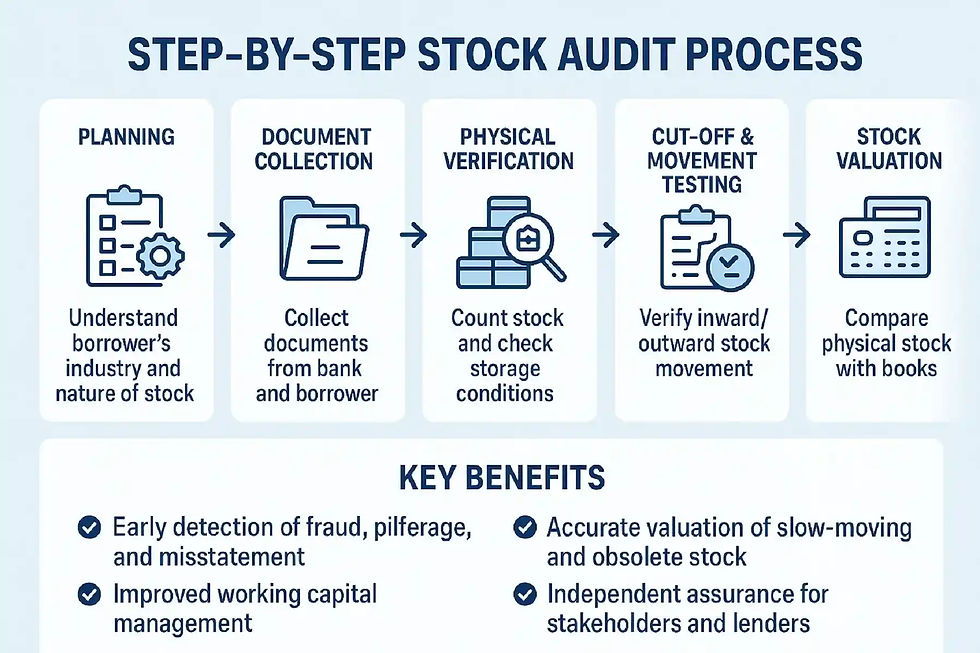
Step-by-Step Stock Audit Process
1. Planning and Scope
Understand borrower’s industry and nature of stock.
Define audit objectives: valuation, compliance, fraud detection, or risk assessment.
2. Document Collection from Bank & Borrower
Bank: Sanction letters, stock statements, DP (Drawing Power) calculations.
Borrower: Purchase/sales registers, invoices, stock registers, GST returns, insurance copies.
3. Physical Verification of Stock
Count raw material, finished goods, consumables, and work-in-progress (WIP).
Check storage facilities and protection against damage.
Verify sealed inventories and third-party stock (agents/warehouses).
4. Cut-off & Movement Testing
Verify inward and outward stock movement.
Scrutinize cut-off procedures to ensure correct recognition of transactions.
5. Stock Valuation & Comparison
Compare physical stock with books of accounts.
Assess valuation method (FIFO, Weighted Average, etc.).
Verify stock-in-transit.
6. Reporting & Discrepancy Analysis
Report pilferage/damage.
Highlight discrepancies between recorded and actual stock.
Recommend corrective actions.
Fact 2: A strong audit mechanism prevents stock overstatement, which is one of the most common reasons for loan defaults in India.
Stock Audit of Bank Borrowers
When businesses borrow working capital loans or cash credit limits, the stock is usually hypothecated to the bank. To ensure security, banks mandate stock audits.
Objectives of Bank Stock Audit:
Ensure borrower’s stock value matches loan security.
Confirm borrower’s compliance with loan terms.
Assess shortfall in Drawing Power (DP).
Highlight risks of fraud or financial misreporting.
Documents Required from Bank:
Sanction letter, DP calculations, stock statements, inspection reports.
Documents Required from Borrower:
Audited financial statements, purchase/sales registers, stock registers, insurance policies, and GST filings.
Fact 3: More than 60% of Indian SMEs rely on cash credit and overdraft facilities secured against stock.
Types of Stock Audits Conducted
1. Physical Condition Audit
Recognition of inventory & WIP.
Disposal of obsolete stock.
Advising storage arrangements to prevent deterioration.
2. Compliance to Process & Procedure Audit
Checking numerical counts and tag sheets.
Random sampling of inward/outward stock.
Verification of cut-off procedures.
3. Associated Processes Audit
Stock at outside locations.
Documentation through photographs.
Use of technology in stock management.
Fact 4: Many banks now mandate geo-tagged stock photos to reduce chances of fraud during audits.
Key Benefits of Stock Audits
Early detection of fraud, pilferage, and misstatement.
Improved working capital management.
Accurate valuation of slow-moving and obsolete stock.
Independent assurance for stakeholders and lenders.
Stronger compliance with RBI, Companies Act, and GST regulations.
Simultaneous audits possible across multiple locations due to audit networks.
Fact 5: Businesses that conduct quarterly stock audits see up to 20% reduction in inventory-related losses compared to those auditing annually.
Common Challenges in Stock Audits
Multi-location operations across India.
Poorly maintained stock registers.
Stock in transit or lying with third-party agents.
Resistance from employees due to fear of exposure.
Difficulty in valuing WIP accurately.
Fact 6: Around 30% of discrepancies in stock audits come from weak internal documentation.
Geographic Importance (Delhi NCR & India-wide)
With India being a manufacturing hub, stock audits hold special importance in Delhi NCR (Noida, Gurgaon, Faridabad) and other industrial belts like Mumbai, Pune, Bengaluru, and Chennai.
Banks in NCR are especially cautious due to large SME financing.
Export houses require stock audits for EPCG compliance.
Multi-location warehouses need synchronized audits for smooth operations.
Fact 7: Delhi NCR contributes to nearly 20% of India’s total MSME output, making it a hotspot for stock audit services.
Practical Insights from Experience
Always conduct surprise verification for accuracy.
Involve technology (RFID, barcoding, ERP integration) for reliable stock counts.
Maintain photographic evidence for banks.
Regularly review insurance coverage to match stock levels.
Fact 8: Digital tools like IoT and AI-based monitoring are increasingly integrated into modern stock audits.
Role of Professional Audit Firms
Specialist firms with an all-India presence can handle multi-location audits, provide unbiased reporting, and ensure standardized procedures. Firms like Ruchi Anand & Associates deploy dedicated stock audit teams that:
Follow strict reporting mechanisms.
Deliver transparent findings.
Cover both business and banking audit requirements.
Fact 9: Large firms often conduct simultaneous audits in 15+ locations across India for banks and corporates.
Conclusion
A stock audit is more than just counting physical goods—it’s about building trust between banks, businesses, and stakeholders. With growing risks of fraud, regulatory scrutiny, and multi-location operations, businesses can no longer afford to ignore this audit.
By conducting regular, professional stock audits, companies can:
Reduce risk,
Improve compliance, and
Build financial credibility.
FAQs on Stock Audits
Q1. Who requires stock audits the most?
👉 Businesses with large inventories, and borrowers availing loans against stock.
Q2. How often should stock audits be conducted?
👉 At least annually, though quarterly audits are recommended for high-volume industries.
Q3. What is stock-in-transit verification?
👉 Checking goods that are dispatched but not yet received in warehouse/books.
Q4. Are stock audits mandatory for bank loans?
👉 Yes, as per RBI guidelines, above certain exposure limits.
Q5. Can technology simplify stock audits?
👉 Yes, ERP, barcoding, and RFID reduce manual errors.
Q6. What industries benefit most from stock audits?
👉 Manufacturing, trading, pharmaceuticals, FMCG, and logistics.
Q7. Who conducts stock audits for banks?
👉 Empanelled Chartered Accountants or professional audit firms.
Q8. Can a stock audit identify fraud?
👉 Yes, it detects overstatement, pilferage, and misuse of funds.
Q9. What is the difference between internal and external stock audit?
👉 Internal audits are done by company staff; external audits by independent auditors for banks/regulators.
Q10. What is WIP in stock audit?
👉 Work-in-progress: partially completed goods valued based on stage of completion.
10 Quick Facts About Stock Audits
Stock audits protect ₹ trillions in bank loans annually.
RBI mandates periodic stock audits for large bank exposures.
60% of Indian SMEs depend on stock-backed loans.
Stock overstatement is a leading cause of loan defaults.
Geo-tagged photos are now common in stock verification.
30% discrepancies come from poor documentation.
Delhi NCR contributes 20% of India’s MSME output.
Quarterly audits reduce losses by 20%.
IoT & AI are transforming audit methods.
Professional firms can audit 15+ locations simultaneously.
Looking for expert Stock Audit services in Delhi NCR and across India? Professional firms with nationwide networks ensure transparent, reliable, and compliant stock verification for your business and banking needs.



Comments